The waste from the Japanese earthquake and tsunami
1. Radioactive contamination
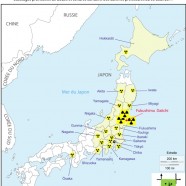
On 11 March 2011 there was a legal vacuum in Japan concerning radioactive waste resulting from a nuclear disaster. Current waste management Law places technical and financial responsibility for waste from natural disasters with local authorities. However, this excludes radioactive waste. The Law on rehabilitation of contaminated soil excludes from its scope radioactive soils and waste. The Law on the management of radioactive materials and waste only concerns those inside the nuclear plants.
The waste from the Japanese earthquake and tsunami
1. Radioactive contamination
On 11 March 2011 there was a legal vacuum in Japan concerning radioactive waste resulting from a nuclear disaster. Current waste management Law places technical and financial responsibility for waste from natural disasters with local authorities. However, this excludes radioactive waste. The Law on rehabilitation of contaminated soil excludes from its scope radioactive soils and waste. The Law on the management of radioactive materials and waste only concerns those inside the nuclear plants.
Oil Spill in the North Sea
Early last week the Gannet Alpha platform situated approximately 180km east of Aberdeen, Scotland started leaking light crude oil into the North Sea. To date it is believed that some 218 tonnes (1,300 barrels) of oil has leaked from an 8 inch thick pipeline which joins Gannet E and F drilling fields. The leak was only confirmed a couple of days after it started by the operator Shell. The platform continues to operate but the sub-sea line between Gannet E and F has been isolated and the flow line depressurised which should reduce the leak flow.
Oil Spill in the North Sea
Early last week the Gannet Alpha platform situated approximately 180km east of Aberdeen, Scotland started leaking light crude oil into the North Sea. To date it is believed that some 218 tonnes (1,300 barrels) of oil has leaked from an 8 inch thick pipeline which joins Gannet E and F drilling fields. The leak was only confirmed a couple of days after it started by the operator Shell. The platform continues to operate but the sub-sea line between Gannet E and F has been isolated and the flow line depressurised which should reduce the leak flow.
“Shipbreaking” #24
49 pages of information on the demolition of ships around the world.
Some excerpts:
– 65 years following the nuclear weapons tests the wrecks from the Bikini Atoll are to be broken up.
– An exclusive report on the incredible end of the Probo family including the Probo Koala responsible for the tragedy in Abidjan precisely 5 years ago.
– The killer asbestos in the top 4 demolition countries.
– The demolition market trends from May to July 2011.
– Are French ship owners taking responsibilities? The scrapping of the Renoir and the Cezanne in Dunkirk and the Tellier in Le Havre.
There is movement in the Arctic
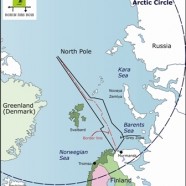
On July 7th 2011 a maritime border agreement between Russia and Norway entered into force. This new dividing line ends a 44 year dispute over 175,000 square kilometres in the Barents and Arctic seas and opens up the former so called “grey zone” for exploration. The day following the entry into force Norway deployed the Harrier Explorer (Imo 7807380) a seismic vessel to start exploration in the zone.
This border agreement follows a Treaty on Cooperation on Aeronautical and Maritime Search and Rescue in the Arctic on May 12th 2011. It is the first legally binding treaty under the circumpolar intergovernmental forum the Arctic Council and was signed in Nuuk Greenland by Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States of America. The Treaty so called the “Nuuk Agreement” is focused on saving lives. It is an important step towards policy-making as there is an increasing amount of traffic venturing into the Arctic, which includes tankers and passenger ships of which a number were not constructed to navigate in ice-covered waters.