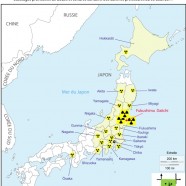
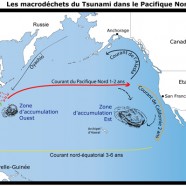
The waste from the Japanese earthquake and tsunami
1. Radioactive contamination
On 11 March 2011 there was a legal vacuum in Japan concerning radioactive waste resulting from a nuclear disaster. Current waste management Law places technical and financial responsibility for waste from natural disasters with local authorities. However, this excludes radioactive waste. The Law on rehabilitation of contaminated soil excludes from its scope radioactive soils and waste. The Law on the management of radioactive materials and waste only concerns those inside the nuclear plants.
Whaling Summit at the Channel Island Jersey
The 63rd annual meeting of the International Whaling Commission (IWC) will take place from July 11th to 14th on the Channel Island Jersey. Robin des Bois would like to take this opportunity to express strong concerns about the deterioration of sanitary state of whales following the tsunami and nuclear accident at Fukushima Daiichi which hit Japan and the North Pacific.
1- Radioactive Pollution
Iodine-131, cesium 137, strontium 90, plutonium are among the identified radionuclides which are spreading across Japanese soil by atmospheric emissions. The Northwest Pacific has become primary recipient for not only liquid discharges coming from Fukushima but also for atmospheric fallout. The sources of whale contamination are multiple: permanent contact with artificial radioactivity, ingestion of contaminated plankton, prey and waste, and the transmission of radioactivity to calves during nursing periods. The external and internal effects of this contamination are potentially mutagenic (mutation of the gene pool), teratogenic (abnormal development of the embryo) and carcinogenic, all very serious impacts on whale populations whose future before the disaster of March 2011 was already menaced.
Millions of Stowaway Passengers Circling Around the Pacific Ocean
The tsunami which followed the Japanese earthquake devastated around 300km of coastal cities, towns, farmlands and greenhouses along Japan’s Pacific coastline. The wave was reported to have spread up to 10km (six miles) inland and inundated around 500km². Not only did the earthquake and tsunami create an estimated 25 million tonnes of rubble, but when the tsunami receded it dragged with it countless quantities of waste in the flooded zone.
The After Shock
Climatic, geological, or anthropogenic natural disasters produce in a couple of seconds, hours or days, enormous amounts of waste, so much so that authorities are unable to handle the quantity with ordinary means. The rupture of “lifelines”, namely water, electricity, transportation routes and communication lines, send survivors into a deep confusion. The accumulation of rubble and waste increases the shock of the populations and postpones the first steps towards the return to normalcy.
The 3 million tonnes of rubble generated by the earthquake in Los Angeles in January 1994 led the city to reinforce and multiply its recycling capacities. Provisional transit and elimination sites for future earthquakes were pre-selected.
A stream of Information
The ocean is still considered as a trash can. Radioactive releases by Japan are increased by a decrease of vigilance. What is occurring in the Pacific Ocean is probably inevitable. However it is not excusable nor should it be viewed as routine as many scientific experts in dispersion and farfetched comparison are currently stating. This type of practice would be impossible in the North East Atlantic. Contracting Parties to the OSPAR Convention follow carefully step by step the slow progression of iodine 131, of cesium 137 and of plutonium released by nuclear installations along the Channel and the North Sea to the Arctic Ocean.
France is to Blame
Thanks to the technological help from France, in 1970 in Tokaï-Mura, south of Fukushima, Japan opened a pilot irradiated fuel-reprocessing factory.
In 1987, Cogema (COmpanie GEnérale des MAtières nucléaires) signed a contract for 1.4 billion francs, equivalent to 213 million Euros, to help construct a new reprocessing factory in Rokkasho-Mura, north of Fukushima – a replica of la Hague’s inland factory near Cherbourg. It should have started service in 2005, but today we are still waiting. As a result, the Fukushima-Daiichi accident site also houses a pool of irradiated fuel, common to the six reactors. The pool is supersaturated and serves as buffer storage pending the start of the Rokkasho-Mura factory. The vice president of Tepco, Tokyo Electric Power Company, declared in 2002 while the local and hostile nuclear referenda were multiplying that “the extraction of plutonium was vital.” The Rokkasho factory must then serve to extract the irradiated plutonium fuel and to re-inject the new fuel associated with the enriched, mixed oxide uranium plutonium fuel. In waiting for the eventual opening of the Rokkasho-Mura factory, France furnished the Japanese reactors with MOX. On March 10th 2011, the day before the earthquake, Areva, the leading French nuclear company, announced to the French High Committee for the Transparence of Information on Nuclear Safety the imminent departure of a new sea transport of MOX between Cherbourg and Japan, which would include fuel for the 3rd reactor at Fukushima-Daiichi.
The Disaster Domain Expands
The extravagant iodine-131 content around the area of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant is a result of leaching of emergency cooling waters used by firefighters and emergency workers. At Fukushima and at French nuclear facilities, there is no collection device for these cooling waters whereas all warehouses storing chemical products are legally bound to be equipped with a collection basin of polluted water used to extinguish fires. The iodine-131 content is also a result of the consequent radioactive dust deposits of the explosions in the heights of the nuclear islets, namely the buildings, the reactors, and the pools. The iodine-131 is one of the indicators of pollution. Other measures will later show similar deviations from standards for cesium-137 and plutonium.
A disaster for dolphins and whales too
Earthquake and Tsunami in Japan
Press release n°11
Several species of large and small cetaceans frequent the coastal waters of eastern Japan and are in the area affected by the liquid and atmospheric radioactive effluent discharged by the Fukushima-Daiichi nuclear power plant.
In particular, this concerns sperm whales, Bryde’s whales, Minke whales, Dall’s porpoises and dolphins. Their lifespan, diet and position at the top of the marine food chain expose them all to the bioaccumulation of chemical and radioactive pollutants.