2017 : The Bastille Day is nuclear
July 14, 2017. (9h26 Paris time).
Unfortunately France and the United States of America have published a joint statement to name the Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons as a nuisance and a threat to World peace. (1)
The Treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons was adopted on July 7, 2017 by 122 States with support of the United Nations. It was inspired by the Convention on the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons initiated by France. It completes the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons and the Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty. The preamble mentions not only the catastrophic consequences of use of nuclear ammunition but also the risk of accidental triggering.
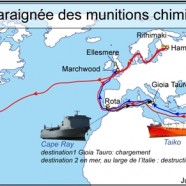
The Cape Ray arrives in Northern Europe
The US Navy chemical factory ship will in the coming days proceed into the Atlantic Ocean and the Bay of Biscay heading towards the North sea.
The Cape Ray is loaded with 6000 tons of chemical aqueous and solid waste issued from the neutralization in the Mediterranean Sea of 560 tons of precursors of the Syrian chemical weapons.
The Cape Ray mission was carried out from July 9th to August 18th. It consisted in diluting precursors of sarin (540t) and of sulfur mustard agent (20t) pulled out of the Syrian territory. Only laconic communiqués from the Pentagon have dotted this sea run neutralization. No circumstantial account of weather conditions, ship spottings, technical uncertainties, air release has been published.
Destruction of Syrian Chemical Weapons (n°5)
According to the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) the most challenging phase towards the destruction of Syrian chemical weapons has just ended with the removal of the last declared precursors and other chemicals from Syrian soil. This first step was constantly delayed in spite of a good knowledge of the associated risks and the participation by numerous State Parties of the OPCW Convention.
However, the next step will enter into unknown territory. The plan is to neutralise 20 metric tonnes of mustard agent and 540 metric tonnes of sarin precursor at sea.
Destruction of Syrian Chemical Weapons n°4
Since the beginning of the year two vessels, loaded with agents for chemical weapons, have been rocking and rolling in the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. There exact location is confidential. The Ark Futura is a 180 meter long RoRo ship operating under the Danish flag. The crew is multinational. The Taiko is a 262 meter long RoRo ship operating under the Norway International flag. In the case of a collision or fire this type of vessel, which can be likened to a floating parking lot, is very vulnerable and will sink quickly.
Inventory of War Remains of Atlantique-Manche Regions from January 1, 2008 to December 31
Inventory of War Remains
Atlantique-Manche Regions
January 1, 2008 – December 31, 2013
Special D-Day Commemoration
June 2014
Sommaire
Introduction
Weapons in the inventory
Sanitary and environmental risk
Inventory of War Remains from January 1, 2008 to December 31, 2013 with maps:
Destruction of Syrian Chemical Weapons n°3
The U.S. Cape Ray is heading towards the Mediterranean Sea.
Its mission is to destroy onboard the so-called priority one substances from Syrian chemical weapons at sea in international waters. For the moment the Field Deployable Hydrolysis System (FDHS) has only been tested, at sea… with water. The FDHS was constructed to be operated on land. Robin des Bois has already voiced opposition to this option favoured by the OPCW and the United States (See information note n°1 and n°2).
The Cape Ray scenario has been put in place to “avoid having to put these materials on somebody’s territory where you have to deal with all the political and environmental conditions associated with doing that under local law” as Mr. Frank Kendall the US. Under Secretary of Defence said early January. However, this option of not neutralising chemical weapons in somebody’s back yard will actually take place in everybody’s back yard. The high seas are the common heritage of mankind.
Destruction of Syrian Chemical Weapons n°2
Neutralizing Syrian chemical weapons on board the Cape Ray, a cargo ship converted into an industrial platform, situated in international waters will make it possible to avoid national regulations.
This worldwide first will transform the high seas into a free zone, free from any democratic controls and environmental and social constraints. The OPCW and the United States state that 500 tonnes of Syrian’s priority substances will be treated at sea in a couple of weeks whereas the final destruction of America’s chemical weapons will not be finished before 2023. On land, the United States is hoping to treat 3,100 tonnes in 10 years. At sea, they are convinced that they can treat 500 tonnes within 4 weeks.
Destruction of Syrian Chemical Weapons
Update January 3, 2014 – 10:15 AM
Treatment of Syrian chemical substances onboard the American ship Cape Ray is a default solution. It follows Northern European countries’ refusal to directly dispose of the precursor chemical ammunition in specialized facilities (*). This operation on the high seas would install industrialization of the world’s oceans.